Transformations of Graphs
Transformations are divided into translations, reflections, and stretches and shrinks. On this page, we will learn these three types.
1. Translations
A translation is a transformation which moves a graph
upward, downward, to the right, or to the left.
a. Vertical translations
There are two types of vertical translations: 1) move a graph upward, 2) shift a graph downward.
Let y = f (x) be an equation of a function, and k be a positive number.
i) Move the graph of y = f (x) upward
The graph of the function defined by y = f (x) + k will be obtained by moving the graph of the function y = f (x) upward by k units.
Example 1. Use the vertical translation to graph of the function defined by y = f (x) + 2.
The picture on the right shows the graph of a function defined by y = f (x). We don't need to know the exact equation.

In the equation, y = f (x) + 2, the positive number + 2 is located after f (x). This means that we shift the graph of y = f (x) upward by 2. Then we will get the red graph shown below.
%20%2B%202.png)
Let y = f (x) be an equation of a function, and k be a positive number.
ii) Move the graph of y = f (x) downward
The graph of the function defined by y = f (x) - k will be obtained by moving the graph of the function y = f (x) downward by k units.
Example 2. Use the vertical translation to graph of the function defined by y = f (x) - 2. Let's use the same graph of y = f (x) in Example 1.
In the equation, y = f (x) - 2, the negative number - 2 is located after f (x). This means that we shift the graph of y = f (x) downward by 2. Then we will get the red graph shown below.
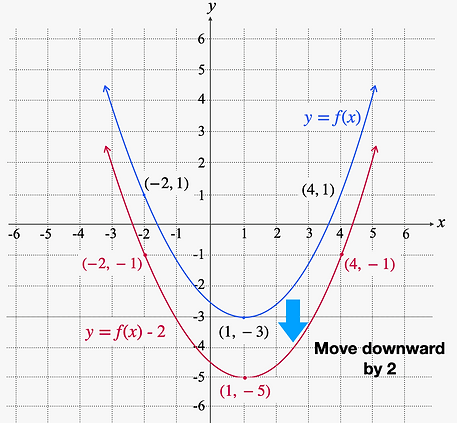%20-%202.png)
In a rectangular coordinate system, the values of y are located on the vertical axis (y-axis). On the y-axis, values increase in the upward direction, and decrease in the downward direction.
The value of k is the only difference between the equation of the original function y = f (x) and the new function y = f (x) + k. A positive value of k affects the value of y, causing the graph of y = f (x) to shift in the upward direction, resulting in the graph of y = f (x) + k.
Similarly, a negative value of -k affects the value of y, causing the graph of y = f (x) to shift in the downward direction, resulting in the graph of
y = f (x) - k.
Question 1. Graph the two functions using the graph of y = f (x) .

(a)
(b)
Table of Contents
1. Translations
a. Vertical translations
i) Shift upward
ii) Shift downward
b. Horizontal translations
i) Shift to the right
ii) Shift to the left
2. Reflections
a. Reflection about the x-axis
b. Reflection about the y-axis
3. Stretches and Shrinks
a. Vertical stretches and shrinks
b. Horizontal stretches and shrinks
References
References
-
Charles C Pinter, A Book of Set Theory, Dove Publication, INC.
-
Karl J. Smith, Nature of Mathematics, 13th edition, Cengage Learning
-
Dave Sobecki and Brian Mercer, MATH in Our World, 15th edition, McGraw Hill
